| Involved partners | IOSB |
| External partners | KIT, UPMC |
| Countries involved in the trials | Germany, France |
| Platforms involved (not finalized) | SensorThingsServer, MORADA, Elasticsearch |
| Number of test users planned | 50 |
The planed trials are using indoor location sensors based on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology to determine the position of a user inside a campus building. The position data will be combined with information systems about work and meeting facilities and optional with other sensor information available for rooms, like air quality or temperature.

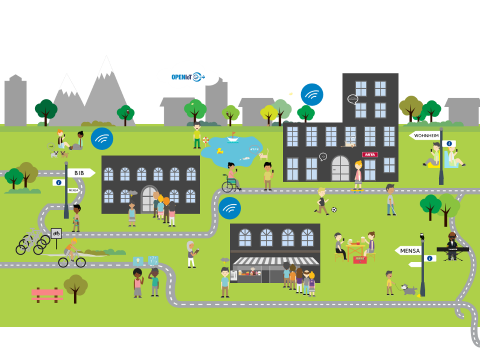
 To create a showcase for the EduCampus vision, we connect to already existing experimentation environments of different campus applications. These platforms are created in order to enable experimentation, and to extend and change the platforms was it would not be possible with an operational system.
To create a showcase for the EduCampus vision, we connect to already existing experimentation environments of different campus applications. These platforms are created in order to enable experimentation, and to extend and change the platforms was it would not be possible with an operational system.
 This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 688156
This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 688156